Pseudocatalase Therapy for Vitiligo
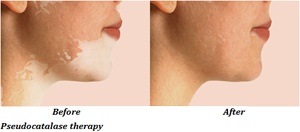
Pseudocatalase is a synthetic topical cream used in the treatment of vitiligo. It is considered that vitiligo may be caused by excessive accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in the upper layers of skin which may cause depigmentation or loss of skin color in patches. In normal conditions, hydrogen peroxide is broken down into water and oxygen by the enzyme catalase. However, in patients with vitiligo, the levels of catalase are less leading to an accumulation of hydrogen peroxide. The pseudocatalase therapy involves application of a cream containing pseudocatalase and calcium among other ingredients which are followed by exposure to narrowband ultraviolet B (NBUVB) radiations. This treatment acts similar to natural catalase and breaks down the hydrogen peroxide thus causing repigmentation.
How is Pseudocatalase applied?
- Apply twice a day to entire affected skin areas
- Only a small amount is needed to cover the area; increasing the frequency and/or amount will not necessarily bring about better results.
- Allow the Pseudocatalase cream to vanish into the skin and completely dry before applying any other topical agents.
- Expose the affected skin to NBUVB light treatments or sun exposure as instructed by your dermatologist.
Patients may begin to see control of pigment loss in 2-4 months. If there is no response after 3 months, the therapy should be stopped and other options evaluated. Treatment may be stopped if full regimentation occurs. This cream can be used to repigment the skin on hands, lips, ears, neck and also on the genital parts.
Treatment with pseudocatalase is considered to be safe with no known systemic side effects.
Schedule your consultation with Dr. Resnik
